Conclusion Of Reflection Of Light: A Deep Dive Into The Science Of Mirrors And Waves
Reflection of light is not just a scientific phenomenon—it’s the reason we can see ourselves in the mirror, why we perceive the beauty of nature, and how communication systems work seamlessly. If you’ve ever wondered how light bounces off surfaces, this article will take you on a journey through the fascinating world of reflection. From the basics to advanced principles, we’ll uncover the magic behind this natural process.
Let’s face it, without reflection, life would be a lot darker—literally and metaphorically speaking. Imagine a world where light doesn’t bounce off objects, making them invisible to the naked eye. Sounds eerie, right? Understanding the conclusion of reflection of light isn’t just about passing science exams; it’s about appreciating the wonders of our universe. So, buckle up, because we’re diving deep into the science of reflection!
Now, before we jump into the nitty-gritty details, let’s set the stage. Reflection of light is more than just a textbook concept—it’s a fundamental principle that governs how we interact with the world around us. Whether it’s using mirrors to check your outfit or relying on fiber optics for high-speed internet, reflection plays a critical role in our daily lives.
What Exactly is Reflection of Light?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. Reflection of light happens when a light wave hits a surface and bounces back. It’s like when you throw a ball against a wall—it comes right back at you, right? Well, light behaves similarly, but on a much smaller scale. This process follows the law of reflection, which states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Pretty straightforward, huh?
But here’s the thing: not all surfaces reflect light in the same way. Some surfaces are smooth, like mirrors, which produce clear reflections. Others, like walls or paper, scatter light in different directions, creating what we call diffuse reflection. So, depending on the surface, the reflection can be sharp, blurry, or even invisible to the naked eye.
Types of Reflection: A Closer Look
Now that we know what reflection is, let’s break it down further. There are two main types of reflection: regular and diffuse. Regular reflection occurs on smooth surfaces, like mirrors, where the reflected light forms a clear image. On the other hand, diffuse reflection happens on rough surfaces, where the reflected light scatters in all directions. Let’s dive deeper into these two types:
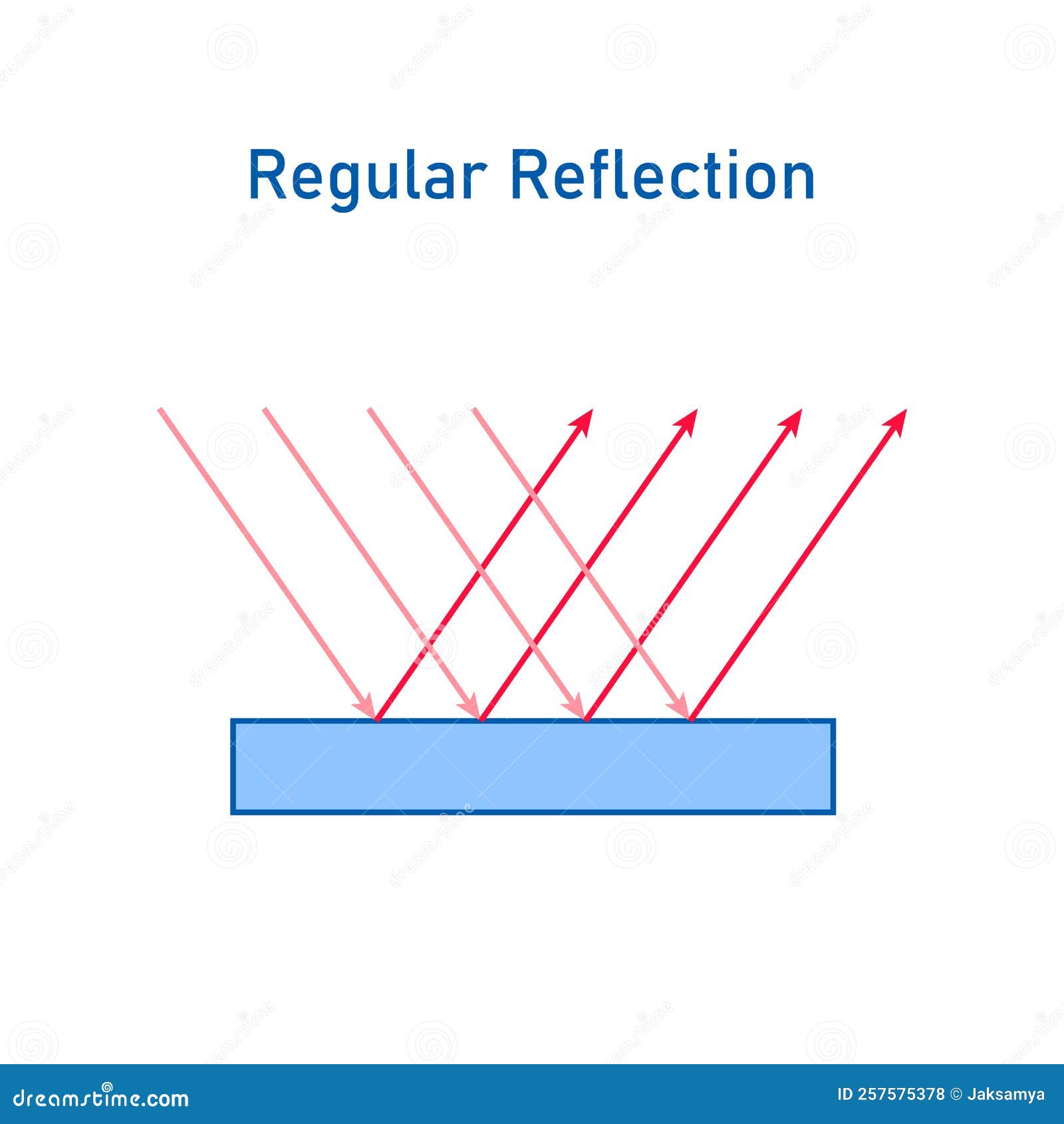
Regular Reflection
This is the kind of reflection you’re most familiar with. When light hits a smooth surface, like a mirror, it bounces off in a predictable way, following the law of reflection. The result? A sharp, clear image that allows you to see yourself or objects clearly. Regular reflection is why mirrors are such an essential part of our daily lives.
Diffuse Reflection
Ever wondered why you can still see objects even when they’re not shiny or smooth? That’s thanks to diffuse reflection. When light hits a rough surface, like a wall or a piece of paper, it scatters in all directions. This scattering allows us to see objects even when they don’t have a polished surface. Diffuse reflection is the reason why we can read books, see paintings, and navigate through our surroundings.
The Law of Reflection: A Simple Yet Powerful Rule
The law of reflection is the backbone of this entire phenomenon. It states that the angle of incidence (the angle at which light hits the surface) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle at which light bounces back). This simple rule governs how light behaves when it interacts with surfaces. Let’s break it down with an example:
- Imagine a ray of light hitting a mirror at a 30-degree angle. According to the law of reflection, the reflected ray will also leave the mirror at a 30-degree angle.
- This principle applies to all surfaces, whether smooth or rough, though the clarity of the reflection depends on the surface’s texture.
Understanding this law is crucial for applications like telescopes, microscopes, and even car headlights. It’s the foundation of many technologies we rely on today.
Applications of Reflection of Light
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s talk about how reflection of light is used in real life. From everyday objects to cutting-edge technology, reflection plays a vital role in various fields. Here are some of the most common applications:
Mirrors
Mirrors are the most obvious example of reflection. They allow us to see ourselves, check our appearance, and even decorate our homes. But did you know that mirrors are also used in scientific instruments, like telescopes and microscopes? Their ability to reflect light makes them indispensable in these fields.
Periscopes
Periscopes are another cool application of reflection. These devices use mirrors to allow people to see over obstacles, like walls or water surfaces. They’re commonly used in submarines and other military equipment, proving that reflection isn’t just for beauty—it’s also for survival.
Fiber Optics
Reflection is the driving force behind fiber optic technology. These tiny glass fibers use internal reflection to transmit data over long distances at lightning-fast speeds. Without reflection, the internet as we know it wouldn’t exist. So, the next time you stream a video or send an email, remember that reflection is working hard behind the scenes.
Reflection in Nature
Nature is full of examples of reflection. From the shimmering surface of a lake to the glowing colors of a butterfly’s wings, reflection is everywhere. Let’s explore some of the most fascinating examples:
Lake Reflections
Have you ever seen the mirror-like surface of a calm lake? That’s reflection in action. When the water is still, it acts like a giant mirror, reflecting the surrounding landscape. This natural phenomenon is not only beautiful but also crucial for the survival of aquatic animals, who rely on light to navigate and hunt.
Animal Adaptations
Some animals have evolved to take advantage of reflection. For example, certain species of fish have shiny scales that reflect light, helping them blend into their surroundings and avoid predators. Similarly, some birds have iridescent feathers that change color depending on the angle of light, making them more attractive to mates.
Reflection and Human Perception
Reflection doesn’t just affect the physical world—it also shapes how we perceive it. Our brains rely on reflected light to interpret the world around us. Without reflection, we wouldn’t be able to see objects, recognize faces, or appreciate art. Here’s how reflection impacts human perception:
Color Perception
When light reflects off an object, it interacts with the object’s surface and reflects certain wavelengths while absorbing others. This interaction determines the color we perceive. For example, a red apple reflects red light and absorbs other wavelengths, making it appear red to our eyes. Reflection is the reason why the world is so colorful.
Depth Perception
Reflection also plays a role in depth perception. Our brains use subtle differences in reflected light to determine the distance and shape of objects. This ability is essential for tasks like driving, catching a ball, or navigating through crowded spaces.
Conclusion of Reflection of Light: Wrapping It All Up
So, what’s the conclusion of reflection of light? Simply put, it’s a fundamental principle that governs how we see and interact with the world. From the mirrors in our bathrooms to the fiber optics powering the internet, reflection is everywhere. It’s a phenomenon that affects both nature and technology, shaping the way we live and work.
Here’s a quick recap of what we’ve learned:
- Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface.
- There are two main types of reflection: regular and diffuse.
- The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
- Reflection has countless applications, from mirrors to fiber optics.
- Nature uses reflection to create stunning visual effects and aid animal survival.
Now that you know the ins and outs of reflection, why not share this knowledge with others? Leave a comment below, or share this article with your friends. Who knows? You might just inspire someone to explore the wonders of science!
References
This article draws on information from reputable sources, including:
- National Geographic
- Scientific American
- Physics Today
These sources provide valuable insights into the science of reflection and its applications in the real world.
Table of Contents
- Types of Reflection
- The Law of Reflection
- Applications of Reflection
- Reflection in Nature
- Reflection and Human Perception
- Conclusion of Reflection of Light
- References
And there you have it—a comprehensive guide to the conclusion of reflection of light. Whether you’re a science enthusiast or just curious about the world around you, this article has hopefully shed some light on the topic. Keep exploring, keep learning, and never stop asking questions!

Reflection Of Light Leverage Edu

reflection of light Free Photo Download FreeImages

Simple Reflection of Light Experiment for Kids
Regular Reflection of Light Diagram. Stock Illustration Illustration